In the vast world of metal materials, steel, with its diverse properties and wide applicability, has become the mainstay in many fields such as industrial production, infrastructure construction, and the manufacturing of daily necessities. Tempered steel, as a product of steel that has undergone special heat treatment, has a profound impact on the development of modern industry.
Tempered steel definition
Tempered steel is a steel obtained by a heat treatment process in which the quenched steel is heated again to a certain range below the critical temperature, kept at a certain temperature for a certain period of time, and then cooled. Although the hardness of the quenched steel is greatly increased, its brittleness is also significantly increased, and there is a large internal stress inside, which makes it have many hidden dangers in practical applications. Tempering treatment is to solve these problems.
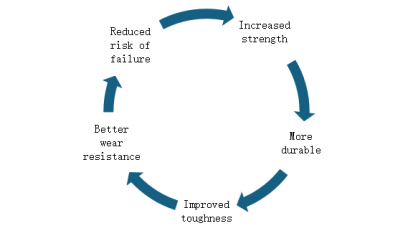
Advantages and characteristics of tempered steel
Good toughness and plasticity
Tempering can effectively improve the brittleness of quenched steel and significantly improve its toughness and plasticity. For example, when manufacturing large structural parts such as bridges and ships, the good toughness of tempered steel can enable it to withstand huge loads and complex stress changes, ensuring the stability and safety of the structure.
Reasonable hardness and strength matching
According to different tempering temperatures and times, the hardness and strength of steel can be accurately controlled. In some occasions with high requirements for hardness and wear resistance, such as tools and molds in mechanical processing, proper tempering can ensure that the steel has sufficient hardness to meet the cutting and forming requirements, and has a certain strength to prevent fracture during work.
Improved dimensional stability
Due to changes in internal organization and the existence of internal stress, quenched steel is prone to dimensional deformation. Tempering can eliminate internal stress and make the organizational structure of steel tend to be stable, thereby effectively improving its dimensional stability.
Enhanced corrosion resistance
Partial tempering process can improve the corrosion resistance of steel to a certain extent. During the tempering process, the structure of the oxide film on the surface of the steel may change and become denser, thereby enhancing the protective effect on the steel matrix and reducing the erosion of the steel by external corrosive media.
Tempering steel processing process
Tempering heating
Put the quenched steel into a heating device, such as a resistance furnace, gas furnace, etc. The heating temperature is accurately set according to the composition of the steel, the quenching state, and the required tempering properties. The heating speed should not be too fast to avoid deformation or cracking of the steel due to thermal stress. During the heating process, it is necessary to ensure that the steel is heated evenly to ensure the consistency of the tempering effect.
Insulation stage
When the steel reaches the predetermined tempering temperature, it is maintained for a period of time to allow the internal structure of the steel to fully transform. The length of the insulation time depends on factors such as the type of steel, the size of the workpiece, the characteristics of the heating equipment, and the tempering temperature.
Cooling process
After the insulation is completed, the steel is removed from the heating equipment and cooled by a suitable cooling method. Common cooling methods include air cooling, oil cooling, water cooling, etc. The cooling rate also has a certain effect on the final performance of the tempered steel.

Types of tempered steel
Low-temperature tempered steel
The tempering temperature is between 150-250℃, which is mainly used to improve the toughness of quenched steel, reduce its brittleness, and maintain a high hardness.
Medium-temperature tempered steel
The tempering temperature is between 350-500℃. The steel tempered at medium temperature has a higher elastic limit and yield strength, and has a certain toughness. Therefore, medium-temperature tempered steel is widely used in the manufacture of various elastic components.
High-temperature tempered steel
The tempering temperature is between 500-650℃. High-temperature tempering is also called quenching and tempering treatment, which can enable steel to obtain good comprehensive mechanical properties, that is, a reasonable match of higher strength, toughness and plasticity.
Application fields of tempered steel
Mechanical manufacturing
In the mechanical manufacturing industry, tempered steel is a key material for manufacturing various mechanical parts. From precision instrument parts to large mechanical equipment parts, such as machine tool bed, guide rails, crane hooks, bridges, etc.
Automobile industry
Many parts of automobiles are inseparable from tempered steel. The engine's crankshaft, connecting rod, camshaft and other key components need to work under harsh conditions of high temperature, high pressure and high speed. The high strength, high toughness and good wear resistance of tempered steel make it an ideal material for these parts. In addition, the springs, half shafts and other parts in the suspension system and braking system of the car are also mostly made of tempered steel to ensure the driving safety and comfort of the car.
Aerospace
The performance requirements of materials in the aerospace field are extremely stringent. The landing gear, engine blades, fuselage structural parts of the aircraft, etc. need to have high strength, light weight and good fatigue resistance. The aircraft landing gear is subjected to huge impact force when landing. The high strength and toughness of tempered steel can effectively absorb the impact energy and ensure the reliability of the landing gear.
Energy field
In energy industries such as petroleum, chemical industry, and electric power, tempered steel is widely used to manufacture various equipment and pipelines. For example, pumping rods in oil extraction, reactors in chemical equipment, valves and flanges in pipeline systems, etc., these components need to operate for a long time in harsh environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and strong corrosion.
Construction industry
In building structures, tempered steel is used to manufacture important load-bearing components such as frame structures of high-rise buildings, steel beams and cables of bridges. For example, in earthquake-prone areas, buildings built with tempered steel can better withstand earthquake disasters and reduce casualties and property losses.

As a metal material that has been carefully optimized through heat treatment, tempered steel plays an indispensable role in various fields of modern industry with its unique performance advantages. Whether in the micro-precision instrument manufacturing or the macro-large-scale infrastructure construction, tempered steel will continue to play its key role and write a new chapter in the application of metal materials.





