In the field of metal manufacturing, chamfers and fillets are two crucial design elements that not only affect the function and performance of the product, but also have an important impact on the safety and aesthetics of the product.
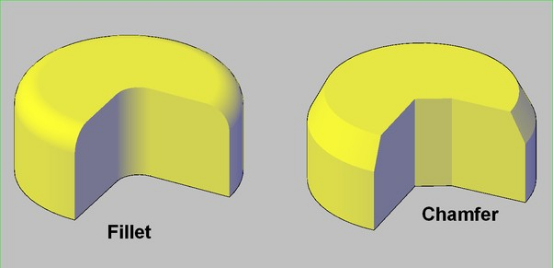
Definition of chamfer and fillet
1. Chamfer
Chamfer refers to removing sharp corners at the edge or corner of a metal part by beveling or grinding to form a plane with a certain angle. The design of chamfer can be adjusted according to specific technical requirements and usage environment.
2. Fillet
Fillet refers to removing sharp corners at the corner of a metal part by arcing to form a circular transition. The radius and shape of the fillet can be adjusted according to design requirements.
Selection strategy of chamfers and fillets
In the metal manufacturing process, the choice of using chamfers or fillets needs to be considered together according to specific design requirements and usage scenarios.
Strength and durability
For parts that bear greater forces and require durability, chamfer design is preferred; in environments with high fatigue resistance requirements, fillet design is more appropriate.
Processing technology
In manufacturing, the treatment methods of chamfers and fillets vary for different metal materials and processing technologies. Choosing the right processing technology (such as forging, milling, stamping, etc.) can affect the final design effect and quality.
Safety and comfort
For metal products involving manual operations (such as tools and instruments), chamfers or fillets are preferred to ensure the safety of operators and comfort of use.

Differences between chamfers and fillets in manufacturing
1. Processing technology
Chamfering
Process method: Chamfers are usually achieved by milling, cutting or grinding. Standard milling cutters or special chamfering tools can be used to cut at specific angles.
Fillet processing
Process method:Fillet processing can be achieved by milling, turning or special fillet tools. In some cases, the use of a grinder may also be necessary.
2. Processing cost
Chamfering
Lower cost: Since the processing process is simple and the required tools and equipment are relatively common, the production cost of chamfers is usually low.
Time efficiency: Chamfers are usually completed in a shorter time and the processing efficiency is high.
Fillet processing
Higher cost: Since special tools and complex processing processes are required, the production cost of fillets is usually higher.
Time efficiency: The time for processing fillets may be longer, especially when processing multiple parts, and the overall efficiency will be affected.
3. Material removal and waste management
Chamfering
Material removal: Chamfering usually only requires the removal of a small amount of material from the edge, so the overall material waste is relatively small.
Waste management: easy to handle, and the utilization rate of scraps is high.
Corner rounding
Material removal: Since the material forming the curved part needs to be removed, the material loss is more obvious than the overall part.
Waste management: The handling of waste is relatively complicated, and the utilization rate of waste may be low.
Application of chamfers and fillets
1. Application of chamfers
Mechanical engineering: In mechanical parts, chamfers can reduce the wear of sharp angles on other parts and reduce the difficulty of assembly. For example, at the connection between gears and shafts, chamfers can avoid damage.
Architectural design: Applying chamfers on the edges and stairs of buildings can improve safety and prevent injuries caused by accidental collisions. In addition, chamfers can also enhance the visual effect of buildings and make the edges look softer.
Furniture manufacturing: The edges of furniture are chamfered to avoid stabbing by milling cutters and increase the beauty and comfort of products.
2. Application of fillets
Product design: In electronic products, fillet design can improve the comfort of holding and reduce damage during falls. In addition, fillet design can improve the beauty of products and make them look more modern.
Safety design: In toys and children's products, fillets can minimize collision damage and protect children's safety.
Architectural design: In the exterior design of buildings, the use of fillets can give people a soft visual effect and better blend with the surrounding environment.
Chamfers and fillets each have their own unique uses and advantages in design. Chamfers are used for simplicity and safety, while fillets are more focused on fluid dynamics and fatigue strength considerations. In metal manufacturing and other engineering fields, designers and engineers should choose between chamfers and fillets based on specific application requirements to achieve the best functional and performance results.
Xuanmin is a metal processing factory with strong technology and excellent design and manufacturing team. Choose us to make your project go further. If you need more information, please feel free to contact our factory, we will serve you wholeheartedly.





