Down milling and reverse milling are two different cutting methods in milling, which are mainly distinguished by the relationship between the tool rotation direction and the workpiece feed direction. They each have their own advantages and disadvantages. In actual processing, the appropriate method should be selected according to the processing conditions and requirements.
Characteristics of down milling operation
The spindle rotation direction is the same as the workpiece feed direction.
The teeth cut into the material from the surface and gradually thin to the bottom of the material.
Advantages
The cutting force direction is favorable: the cutting force presses the workpiece against the worktable, improving the processing stability.
High surface quality: the chips are thicker at the end of the battle, the tool is not easy to slip, and the surface finish is improved.
The tool is long: the tool cuts more smoothly, reducing friction and heat accumulation.
Disadvantages
High machine tool rigidity requirements: due to the cutting force pushing the workpiece against the spindle, it is easy to cause vibration or feed instability.
High torque requirements: clamping is required to prevent the workpiece from moving due to cutting force.
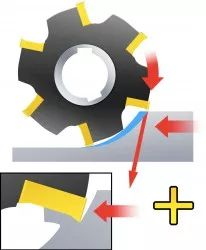
Features of reverse milling (conventional milling) operation
The spindle rotation direction is opposite to the workpiece feed direction.
The teeth cut into the material from the bottom and gradually thicken to the surface of the material.
Advantages
The machine tool spindle is strong: the cutting force pulls the workpiece to the worktable, and the feed system is more stable.
Lower requirements for the lower part: the direction of the cutting force has less clamping pressure, which can easily cause the workpiece to loosen.
Disadvantages
Massive surface destruction: the tool easily slides on the workpiece surface when cutting in, causing slight vibrations.
Unfavorable direction of cutting force: It is more likely to cause tool damage or material deformation.
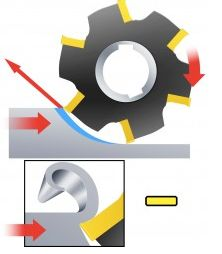
Factors to consider when choosing down milling or reverse milling
Machine tool spindle: High rigidity and spindle machine tools are suitable for down milling.
Workpiece material: Hard materials are preferred to reverse milling, while soft materials are more suitable for down milling.
Surface requirements: Down milling is preferred when high surface quality requirements are required.
Workpiece conditions: Reverse milling is optional when the workpiece is not fixed during transportation.
Correctly selecting down milling and reverse milling methods is conducive to improving processing efficiency, ensuring processing quality, and extending tool life.
Application scenarios of down milling
1. Processing with high surface quality requirements
Down milling has a smooth cutting process, and the cutting force presses the workpiece against the worktable, so the surface quality is high, which is suitable for processing with strict requirements on the surface roughness of the workpiece.
Application: Finishing of soft materials such as aluminum alloy and copper, and mold surface processing.
2. Processing of soft materials
The cutting direction of down milling is conducive to chip flow and reduces material deformation. It is suitable for processing tough materials such as aluminum and plastic.
Application: Processing of workpieces and plastic products in the aviation industry.
3. CNC machining (CNC)
Highly rigid CNC machine tools are suitable for down milling, especially when the cutting path planning is accurate, the advantages of down milling can be maximized.
Application: Simulation processing of complex parts, 3D surface processing.
4. Thin-walled parts processing
The cutting force of down milling presses the workpiece against the supporting surface, which is conducive to reducing the vibration and deformation of thin-walled parts.
Application: Electronic equipment housing, sparse parts.

Application scenarios of reverse milling
1. Insufficient rigidity of machine tools or old equipment
The direction of the reverse milling cutting force pulls the workpiece toward the worktable, which is suitable for old and poorly rigid equipment to avoid vibration and instability of the feed system during processing.
Application: Ordinary milling machine processing used in small workshops.
2. Rough processing of hard materials
When processing hard materials, the reverse milling cutting force is small, and the initial cutting can better break through the surface heat treatment layer of the material.
Application: Removal of oxide scale on the surface of castings, processing of steel blanks.
3. Uneven or burred materials
The cutting direction of the reverse milling tool helps to avoid vibration caused by burrs or surface irregularities.
Application: Cast iron parts processing, untreated blanks.
4. Unstable clamping workpieces
The direction of the cutting force of reverse milling is conducive to keeping the workpiece unstable, which is suitable for processing scenarios with limited constraints.
Application: Temporarily occupied parts or large workpieces.

Climb milling and reverse milling each have their own unique advantages and applications. Climb milling is usually used for finishing and applications that require high surface quality. In actual manufacturing, the choice of Climb milling or reverse milling should be determined according to different situations. At Xuanmin, we provide comprehensive CNC machining services in China, including CNC milling, turning, and more. We simplify the process of sourcing custom parts, making procurement faster, easier, and more efficient!





