Pressure casting technology is one of the casting processes in modern manufacturing. It is widely evaluated in many fields such as automobiles, electronics, and aviation for its high efficiency and high quality. Among them, low-pressure casting and high-pressure casting are two important pressure casting processes. Understanding the characteristics, differences, and application scenarios of these two processes not only helps to optimize production options, but also better meet the quality and performance requirements of different products.
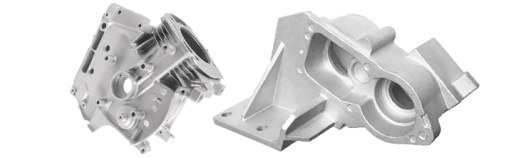
Concept of Low-Pressure Die Casting
Low-pressure casting uses gas pressure (usually 0.1-0.2 MPa) to slowly inject catalyst metal from a closed container into the mold through a runner system until the cavity is filled and the casting is formed.
Features and advantages of low-pressure casting
Suitable for thin-walled complex structures: Low-pressure casting has a slow metal filling speed and is suitable for castings with complex shapes and uniform wall thickness.
Oxygen pore defects: Stable pressure and slow injection speed make the metal more fluid and have fewer pores and inclusions inside the casting.
High-quality surface and mechanical properties: It can produce high-quality aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy castings, especially widely used in automobile and aviation parts.
Cost control: mold life, suitable for mass production.

High-pressure casting concept
High-pressure casting is a casting process that uses high pressure (usually 10 MPa) to quickly inject metal into a steel mold and cool it in a short time.
Features and Benefits of High-pressure casting
High Efficiency: Rapid injection and cooling are suitable for mass production, and the production efficiency is extremely high.
Complex Shapes and Thin-Walled Castings: High-pressure injection enables metal to fill complex mold details, suitable for thin-walled castings.
High Surface Quality: Smooth surface, less need for post-processing.
Adapt to a variety of metals: magnesium alloys, zinc alloys and magnesium alloys are commonly used in high-pressure casting.Limitations.The casting is prone to tiny pores, which limits the application of heat treatment or high strength requirements.The mold wears faster and the cost is higher, which is suitable for mass production.

Comparison of low pressure and high pressure casting
| feature | Low pressure casting | High Pressure Casting |
| Pressure | Low pressure, 0.1-0.2 MPa | high pressure, usually more than 10 MPa |
Filling speed | Slow, reduce pores and inclusions | Fast, suitable for complex structures and work requirements |
Production efficiency | Large-scale, suitable for large-scale batch production | High efficiency, suitable for mass production |
Casting quality | Better performance, less pores, suitable for mechanical heat treatment | Good surface quality, but contains tiny pores |
| Mold life | Longer, lower cost | Fast wear, high mold cost |
Application of low pressure casting
Automotive industry: an important process for key components such as aluminum alloy wheels, engine cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, pistons, gearbox housings, etc. These components need to withstand high temperatures, high pressures and complex working environments, and have strict requirements on the mechanical properties, air tightness and corrosion resistance of the materials.
Aerospace: In the field of aerospace, castings need to withstand extreme working environments such as high temperatures, high pressures, strong corrosion, etc.
Mechanical manufacturing: In the field of mechanical manufacturing, it can produce a variety of complex mechanical parts and components, such as gears, bearing seats, pump bodies, etc.
Electronic and electrical appliances: In the electronic and electrical industry, low pressure casting can be used to produce components such as radiators and motor housings. These components need to have good heat dissipation performance and mechanical strength to ensure the normal operation and long life of electronic equipment.
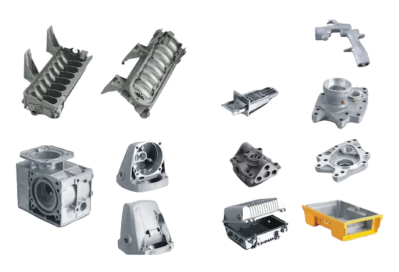
High pressure casting application areas
Automotive industry: engine block, body shell, body frame (such as door frame, instrument panel bracket, etc.).
Electronic products: smart phone shell, TV shell, laptop shell, etc.
Consumer products: power tool shell, household appliance shell, LED lamps, etc.
Industrial products: mechanical equipment housings, building aluminum alloy parts, etc.

Low-pressure casting is suitable for small and medium batches, large-sized or complex-shaped castings, with good surface quality and low defect rate. High-pressure casting is suitable for mass production, thin-walled castings and parts with high precision requirements, especially some castings with complex shapes and short production cycles.
Do you have any questions about the process? Contact Xuanmin kindly. You can also upload your design to get a quote now and learn how we can support your die casting needs.





